Minoxidil is a treatment that’s proven to slow hair loss and improve symptoms of male pattern baldness, female pattern hair loss, and many other types of alopecia [1-2]. It’s available as a tablet — oral minoxidil — or as a topical solution.
Oral minoxidil and topical minoxidil have a similar mechanism, but they target different areas. While topical minoxidil only affects the area to which it’s applied, oral minoxidil affects the whole body. So it may be more effective, but also puts you at a heightened risk of systemic side effects.
So which is right for you and your hair loss: oral minoxidil vs topical? Let’s weigh up the pros and cons of each to discover whether you’re better suited for oral or topical minoxidil.
Table of Contents
- How does minoxidil work?
- Oral minoxidil vs topical: head to head
- Side effects of oral vs topical minoxidil
- Effectiveness of oral vs topical minoxidil
- Availability of oral vs topical minoxidil
- How to take oral vs topical minoxidil
- Which is right for you: oral or topical minoxidil?
- Get minoxidil at the best price from DrHair
- FAQs
How does minoxidil work?
Minoxidil is primarily a vasodilator. It opens up the blood vessels, allowing blood to flow more freely. When used on the scalp, topical minoxidil stimulates extra blood flow to the hair follicles, bringing essential nutrients that help with hair growth.
Oral minoxidil dilates the blood vessels throughout the body. It’s primarily used as a treatment for high blood pressure, but its full-body impact can also help with hair growth on the scalp and elsewhere.
Oral minoxidil vs topical: head to head
Take a look at the table below to see how oral vs topical minoxidil measure up against each other at a glance:
Oral minoxidil | Topical minoxidil | |
Licensed for hair loss? | No | Yes |
Treatment time | Takes 3-6 months to see initial results | Takes 3-6 months to see initial results |
How to use it | Once-daily tablet | Twice-daily spray, solution or foam |
Side effects | Can affect the whole body | Can affect the area where it’s applied (and surrounding areas) |
Who can use it | Anyone with suitable types of hair loss, especially if topical minoxidil hasn’t worked | Anyone with suitable types of hair loss |
Who shouldn’t use it | Those who are pregnant or breastfeeding Those taking medication that affects blood pressure Those with certain underlying conditions (see below) | Those who are pregnant or breastfeeding |
Effectiveness | A 2024 study found 5 mg oral minoxidil to be as effective as 5% topical minoxidil in those with male pattern baldness [1]. May be more effective for treating crown hair loss [1] | A 2024 study found 5% topical minoxidil to be as effective as 5 mg oral minoxidil in those with male pattern baldness [1] |
UK availability | Off-label (prescription needed) | Over-the-counter (no prescription needed) |
Side effects of oral vs topical minoxidil
Topical and oral minoxidil both have side effects, but the side effects of oral minoxidil are more significant than those associated with topical minoxidil. So it’s usually best to stick with topical minoxidil unless it doesn’t give you the results you want.
Side effects of topical minoxidil include itchiness, skin irritation, and occasionally a minoxidil rash. These minoxidil side effects are localised and usually only affect the area of application. Women using minoxidil may see hair growth on unwanted areas of the face when using higher concentrations (2% minoxidil is normally recommended for women).
Oral minoxidil side effects can affect the whole body, rather than just the area of application. Side effects of minoxidil tablets include:
- Hypertrichosis (excessive facial and body hair growth)
- Low blood pressure
- Dizziness and feeling lightheaded
- Fluid retention
- Tachycardia (increased heart rate)
- Headaches
- Insomnia
In most cases, side effects will subside either with continued use or if you stop using the treatment. If you do choose to stop minoxidil, you’re likely to lose any hair you’ve gained.
Effectiveness of oral vs topical minoxidil
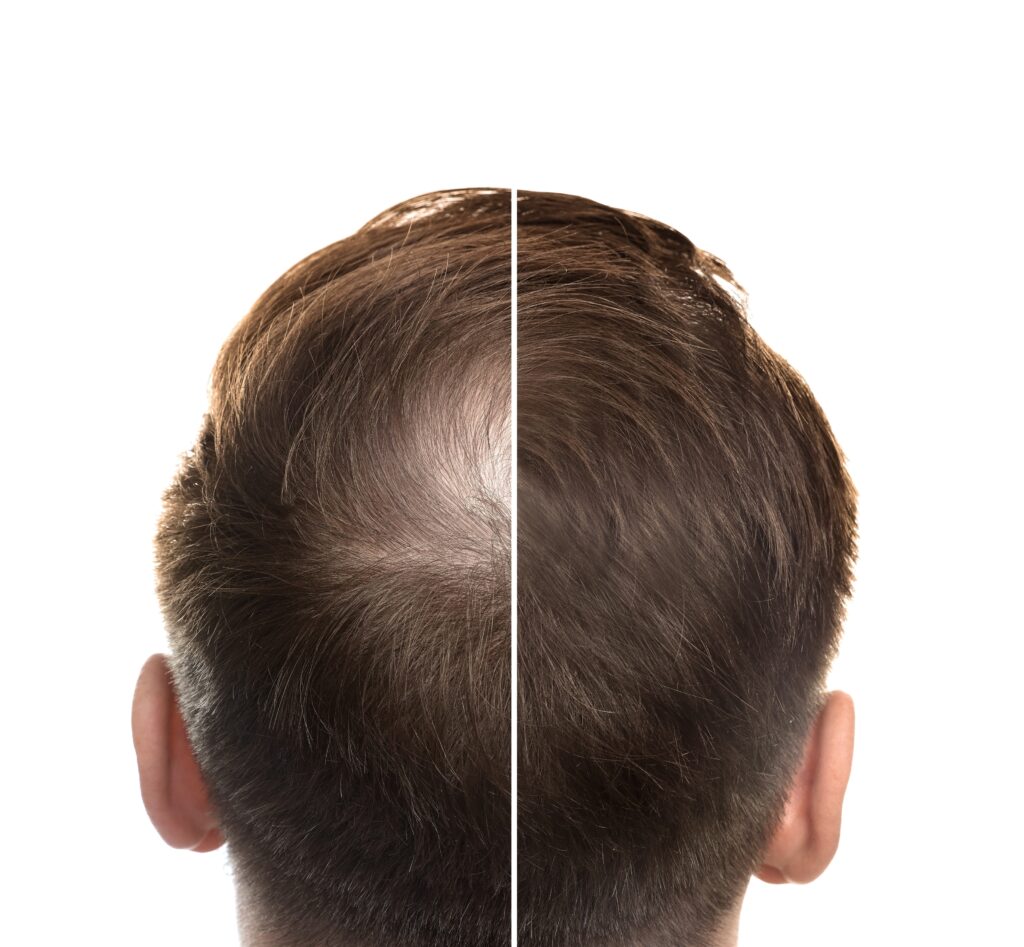
While oral minoxidil is generally considered to be more potent and therefore more effective than topical minoxidil, studies have shown that the effectiveness is similar over 5-6 months of treatment [1-2]. Oral minoxidil (5 mg) was found to be more effective than topical minoxidil for treating crown hair loss, but not frontal hair loss [1].
Availability of oral vs topical minoxidil
Topical minoxidil is available without a prescription in the UK. Oral minoxidil, however, is normally only prescribed as a treatment for high blood pressure. But you can get it prescribed off-label as a hair loss treatment if you’re eligible.
While most people can use topical minoxidil (it’s normally safe as long as you’re not pregnant or breastfeeding), there are some contraindications for oral minoxidil. You shouldn’t take oral minoxidil if you have:
- High blood pressure
- Cardiovascular disease, including a history of stroke
- Kidney problems
- Heart problems, including heart failure and a history of heart attacks
If you’re unsure, speak to your GP to see if you’re a good candidate for treatment with oral minoxidil. Our team of doctors can also help — just book a consultation to discuss your eligibility.

Recommended
Finasteride (1mg) + Minoxidil 5% (60ml)
Inhibit DHT production to halt hair loss and promote hair growth.
How to take oral vs topical minoxidil
Oral minoxidil is a pill you take once a day. You may be prescribed different dosages depending on your needs.
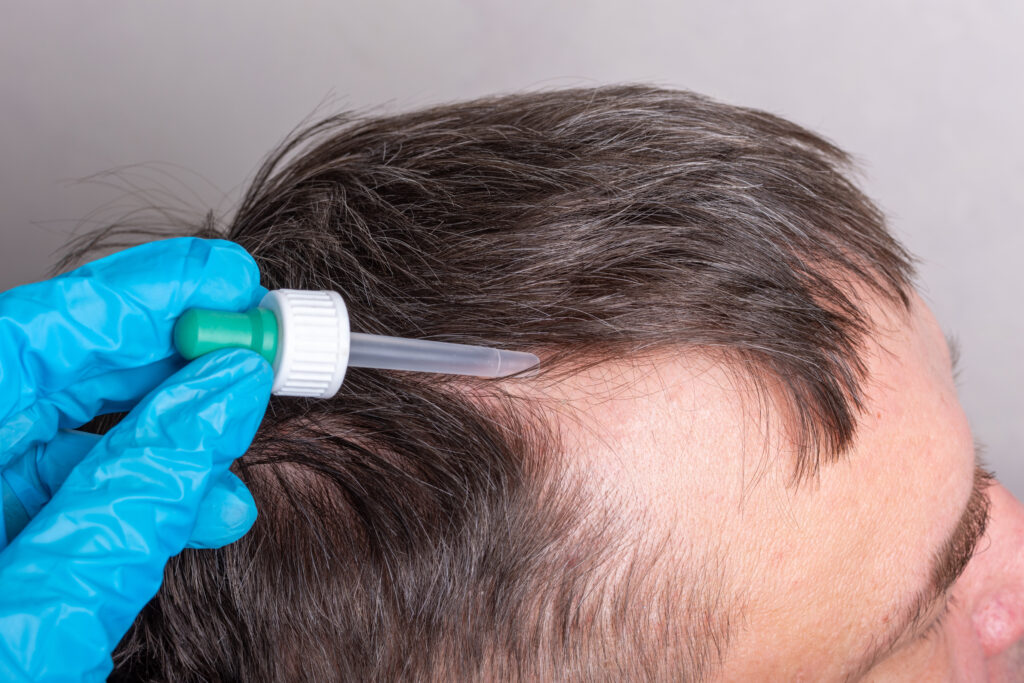
Topical minoxidil is available as a spray, foam, or dropper solution. You’ll normally apply 1 ml of product to your balding areas twice a day (once in the morning, once in the evening). Find out how to apply minoxidil depending on which product type you have, and how often to apply minoxidil.
Which is right for you: oral or topical minoxidil?
Both types of minoxidil have pros and cons. Let’s take a look so you can decide whether oral vs topical minoxidil is the right option for you.
Oral minoxidil pros and cons
+ Convenient and easy to take
+ May be more effective for crown hair loss
+ Lower risk of localised side effects
+ Available in different doses
– Not available over-the-counter
– Higher risk of systemic side effects
– Not suitable for those with certain medical conditions
Topical minoxidil pros and cons
+ Available without prescription
+ Available in different concentrations
+ Lower risk of systemic side effects
+ Most people can safely use it
– Takes longer to apply
– Higher risk of localised side effects
Whether you opt for oral or topical minoxidil depends on your priorities. Most people start with topical minoxidil to minimise the risk of systemic side effects, then switch to oral minoxidil if they don’t see the results they want.
Get minoxidil at the best price from DrHair
Our 5% minoxidil formula is available from DrHair at the best price. Online assessment takes less than a minute, so you can check your eligibility for your chosen hair loss products quickly and easily. You’ll also get:
- Fast discreet delivery
- Treatment from industry-leading suppliers
- More flexibility with subscription-free treatment options
- Lower prices when you subscribe for up to 12 months
Take our one-minute topical minoxidil assessment to get started.
FAQs
Learn more about oral vs topical minoxidil in these frequently asked questions.
Clinical evidence suggests oral minoxidil and topical minoxidil offer similar results [1-2]. But in practice, oral minoxidil may be recommended if topical minoxidil doesn’t work. It also has a higher risk of systemic side effects, so it’s not necessarily better than topical minoxidil, but it offers different benefits.
No. You’re unlikely to see any benefit from using both oral and topical minoxidil at the same time, and you’ll have a higher chance of experiencing side effects (both systemic and localised). So it’s best to stick with either oral or topical minoxidil.
Yes. Minoxidil is often combined with finasteride for men with male pattern baldness. Choose from oral finasteride + topical minoxidil or a combined topical finasteride + minoxidil formula.
Take a look at clinical finasteride and minoxidil results to see the impact of combining these treatments.
Studies suggest it’s unlikely that switching from topical to oral minoxidil will cause hair loss [3]. So you shouldn’t need to worry about dread shed coming back if you choose to move from topical to oral minoxidil.
Yes, oral minoxidil can increase body hair growth. This may not be an issue for men, but women may want to avoid this. Using topical minoxidil or a lower dose of oral minoxidil may reduce excess body hair growth.